Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet
Price 8000 INR/ Box
Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet Specification
- Dosage Form
- As Per Suggestion
- Origin
- India
- Feature
- Other
- Ingredients
- Other
- Application
- Other
- Storage Instructions
- Cool & Dry Place
- Shelf Life
- 2 Years
Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Box
- Payment Terms
- Letter of Credit at Sight (Sight L/C), Paypal, Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque, Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Boxes Per Day
- Delivery Time
- 1 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Within a certain price range free samples are available
- Packaging Details
- As per requirement.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, South America, Middle East, Africa, Western Europe, Central America, Asia, Eastern Europe, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet
The Following are Some Important Aspects of Sorafenib Tosylate Tablets:
Indications: Hepatocellular carcinoma and advanced renal cell carcinoma are the two cancers that sorafenib is most commonly used to treat. In clinical studies or off-label for other cancers, it may also be applied.
Dosage: Depending on the kind of cancer being treated, the patient's medical history, and other factors, the dosage of Sorafenib Tosylate may change.
Administration: A glass of water should be consumed together with the tablet(s). The prescribing oncologist will set the precise dose regimen and length of treatment.
Diarrhea, weariness, hand-foot skin reaction (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia), rash, elevated blood pressure, and changes in hair color or texture are typical adverse effects of sorafenib tosylate. Any adverse effects that are alarming should be brought up with the healthcare professional.
Before beginning Sorafenib treatment, patients should tell their doctors about any additional drugs, dietary supplements, or health issues they may have in order to prevent any potential drug interactions or complications.
Monitoring: To manage potential adverse effects and assure the drug's efficacy, regular medical exams and monitoring of blood pressure and liver function are usually done while taking sorafenib.
Benefits of Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet
1. Treatment of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma, the Most Common Type of Liver Cancer: Sorafenib Tosylate is indicated for the treatment of advanced HCC, the Most Common Type of Liver Cancer. It has been demonstrated to improve overall survival, prolong the time until tumor progression, and reduce the disease's course in some individuals.
2. Sorafenib tosylate is also employed in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a form of kidney cancer. In some patients, it can increase progression-free survival and assist halt tumor growth and spread.
3. Prolonged advancement-Free Survival: Sorafenib tosylate has been demonstrated to slow the advancement of the disease in some cancer patients, allowing them to live longer with a higher quality of life.
4. Reduced Tumor Angiogenesis: Sorafenib tosylate can slow the growth of tumors by reducing the development of blood vessels that supply them with nutrition. This is accomplished by targeting the signaling pathways involved in angiogenesis.
5. Adjuvant Therapy: Sorafenib tosylate may occasionally be administered to lower the risk of cancer recurrence following surgical excision of the tumor.
6. Potentially Well-Tolerated: Targeted medicines like Sorafenib tosylate frequently have a more favorable side effect profile than conventional chemotherapy, making them more bearable for some patients.
FAQ of Sorafenib Tosylate Tablet
Sorafenib tosylate should be taken exactly as directed by your doctor. It is often taken twice daily, either before or after meals. It's crucial to consume the tablet whole, without crushing or chewing it, along with a full glass of water.
3. What should I do if I forget to take a dose?
Sorafenib tosylate should be taken as soon as you remember if you miss a dose. If your next dose is approaching, skip the missed one and carry on with your regular dosing regimen. To make up for a missing dose, do not take a second one.
4. Does the sorafenib tosylate pill have any adverse effects?

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Anti Cancer Medicine Category
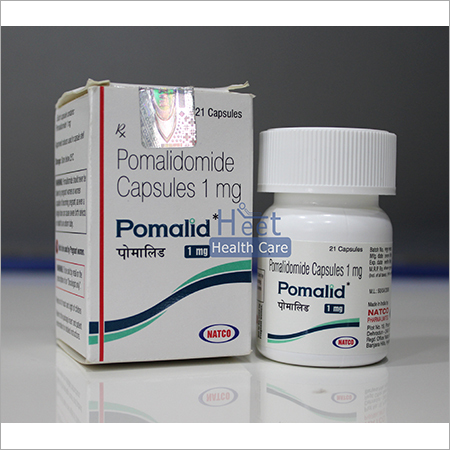
Pomalid Pomalidomide 1mg
Price 9000 INR / Box
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Boxes
Storage Instructions : Cool & Dry Place
Dosage Form : As Per Suggestion
Origin : India
Feature : Other
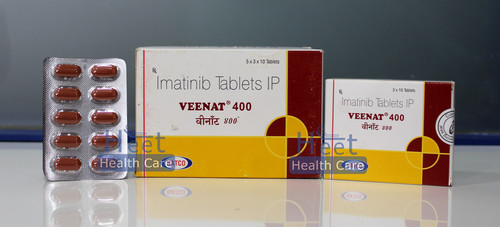
Veenat Imatinib Mesylate 400mg Tablets
Price 2500 INR / Box
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Boxes
Storage Instructions : Cool & Dry Place
Dosage Form : As Per Suggestion
Origin : India
Feature : Other
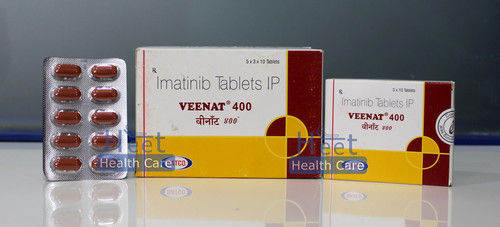
Veenat Imatinib 400 mg Tablets
Price 2500 INR / Box
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Boxes
Storage Instructions : Store Imatinib Tablets in a cool, dry place, away from direct heat and light.
Dosage Form : As Per Suggestion
Origin : India
Feature : Other
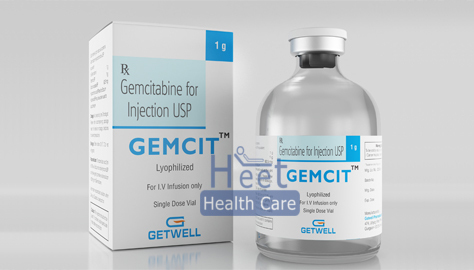
Gemcitabine Injection Ip 200 Mg
Price 450 INR / Box
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Boxes
Storage Instructions : Cool & Dry Place
Dosage Form : As Per Suggestion
Origin : India
Feature : Other
 |
HEET HEALTHCARE PVT. LTD.
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry